Introduction: Taxes are Part of the Game
Investing is about growing your money, but it is also about keeping more of it. And that means understanding how your investments are taxed. Too many investors ignore taxes until April rolls around. And by then, it is too late to plan smart. This lesson will help you:
Capital Gains Tax Basics
When you sell an investment for more than you paid, that profit is called a capital gain, and it is taxable. Two Types of Capital Gains: Short-Term: Investments held one year or less. Taxed at your regular income tax rate Long-Term: Held more than a year Taxed at lower, favorable rates (e.g., 0%, 15%, or 20% in the U.S.) Key Points: Example: You buy stock for $5,000 and sell it for $8,000: Holding longer is not only safer, but also smarter for your tax bill.
Dividends and Interest Income
Selling your investments is one way to profit from them, but they can also pay you along the way. However, just like gains, that income can be taxed differently depending on the type. Dividends: Taxed at long-term capital gains rates (lower) Taxed as regular income Interest Income: Why This Is Important: Not all income is created equal, which is why it is crucial to know what you’re earning and how it is taxed.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts
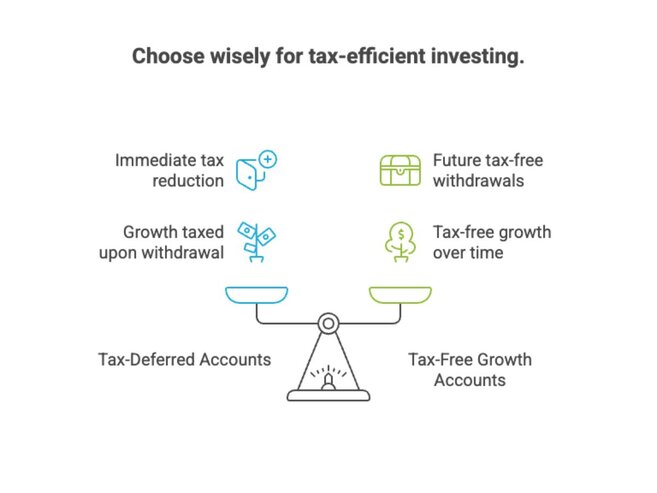
One of the smartest ways to lower your tax burden is to use accounts designed to help you invest tax-efficiently. Depending on the type, these accounts either delay taxes, reduce them, or eliminate them altogether. Common Types: 401(k) / RRSP (Tax-deferred) Roth IRA / TFSA (Tax-free growth) Traditional IRA (Similar to 401(k), but for individuals) Key Advantages: Know Your Limits: These accounts are the tax shelters for everyday investors, and one of your most powerful tools.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting is a clever way to use investment losses to your advantage - to reduce your tax bill.
How It Works:
- You sell an investment at a loss
- That loss offsets gains from other investments
- If losses exceed gains, you can deduct up to $3,000 against ordinary income (U.S.)
But There Are Rules:
- Wash Sale Rule: You can’t buy the same or “substantially identical” investment 30 days before or after the sale
- You can still stay invested by buying a similar (but not identical) asset
Why This Is Important:
- Reduces your taxable gains
- Helps smooth out the tax impact of rebalancing
- Can boost after-tax returns over time
You don’t need to ‘win’ every trade. Even losses can work for you with the right strategy.
Quiz
Which type of account lets your investments grow and be withdrawn tax-free?
a) Traditional IRA
b) Roth IRA
c) Savings account
What’s the main benefit of tax-loss harvesting?
a) It increases your capital gains
b) It offsets investment losses with gains
c) It reduces your tax bill by using losses
3. How are qualified dividends taxed?
a) At the long-term capital gains rate
b) They're tax-free
c) At your regular income tax rate
See the answers at the bottom
Exercise:
You invest $5,000 in two accounts:
- One in a taxable brokerage account
- One in a Roth IRA
After 10 years, both accounts grow to $10,000.
If you sell both investments at that point, which one lets you keep more?
See the answers at the bottom
Summary and Key Takeaways
- Capital gains are taxed differently depending on how long you hold; long-term usually means a lower rate.
- Dividends and interest can trigger taxes even if you don’t sell anything.
- Tax-advantaged accounts like Roth IRAs and 401(k)s can protect your growth from taxes. Use them wisely.
- Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy to turn losses into tax benefits.
- Planning ahead can help you keep more of what you earn, which makes a big difference over time
Answers to the Quiz and Exercise Questions
Quiz Answers:
1) Which type of account lets your investments grow and be withdrawn tax-free?
Answer: b) Roth IRA
2) What’s the main benefit of tax-loss harvesting?
Answer: c) It reduces your tax bill by using losses 3) How are qualified dividends usually taxed? Answer: a) At the long-term capital gains rate Exercise Answers: The Roth IRA, because withdrawals are tax-free. In the taxable account, you’d owe capital gains tax on the $5,000 gain.
Additional resources
This section contains helpful links to related content. It isn’t required, so consider it supplemental.
-
It looks like this lesson doesn’t have any additional
resources yet. Help us expand this section by contributing
to our curriculum.
